

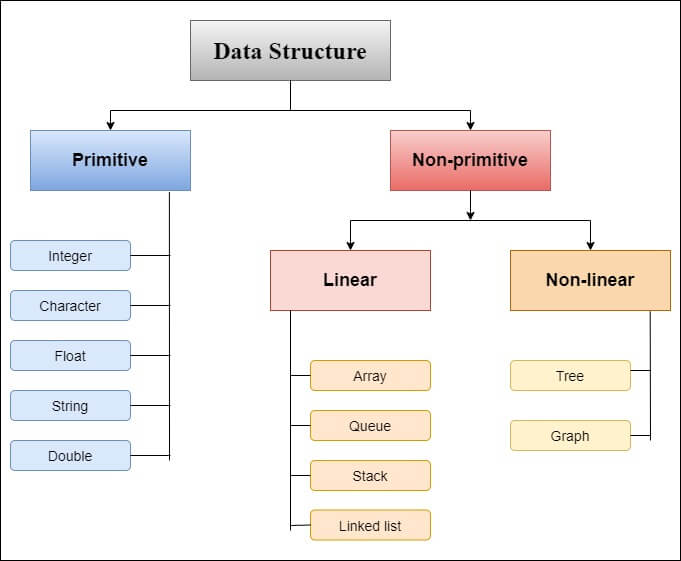
Learn more about String data structure in this link.Learn more about Map data structure in this link.Learn more about Set data structure in this link.Learn more about List data structure in this link.For example, Using Set to store many unique data or using Map to store a data with key value pairs. Make sure to use the data structure based on the requirement. For example in this code: (name + ": " + email) The String can be concatenated using + operator. This is the substring(begin, end) mechanism in String. Get the String value from beginning index until the end indexĬoncatenate the String with the given String (str)Ĭheck if a given String (str) is equals with the compared StringĬheck if a given String (str) is equals with the compared String but the case is ignored Get the String value from beginning index You will learn more about Linear and Non-linear Data Structures in subsequent lessons.Convert all the characters into uppercaseĬonvert all the characters into lowercaseĬheck if a given character or String (str) is exists inside String Graph: In this case, the data sometimes has relationships between pairs of elements, which do not necessarily follow a hierarchical structure. The data structure that represents this relationship is called a rooted tree graph or tree. Tree: In this case, the data often has a hierarchical relationship between the different elements. This structure mainly represents data with a hierarchical relationship between different elements.Įxamples of Non-Linear Data Structures are listed below: The typical examples of the linear data structure are: These linear structures are called linked lists. The second technique provides a linear relationship between all the elements represented using the concept of pointers or links.These linear structures are called arrays. The first way is to provide a linear relationship between all the elements represented using a linear memory location.There are two techniques for representing such linear structure within memory. Non-linear Data Structure Linear Data StructureĪ data structure is said to be linear if its elements combine to form any specific order.Categories of Data Structureĭata structures can be subdivided into two major types: Second, the formation should be so simple that one can efficiently process the data whenever necessary.
First, it must be loaded enough into the structure to reflect the actual relationship of the data with a real-world object.The variety of a specific data model depends on the two factors: The data can be managed in many different ways, such as a logical or mathematical model for a particular organization of data is called a data structure. In the context of computers, the data structure is a specific way of storing and organizing data in the computer's memory so that these data can be easily retrieved and efficiently used when needed later. The example mentioned above, such as ID, Age, Gender, First, Middle, Last, Street, Area, etc., are elementary data items, whereas the Name and the Address are group data items. But an ID assigned to a student will usually be considered a single item. Let's take an example where a student's name can be broken down into three sub-items: first, middle, and last. The data items are then classified into sub-items, which is the group of items that are not called the simple primary form of the item. Data is simply a collection of facts and figures, or you can say that data is a set of values or values in a particular format that refers to a single set of item values. In the modern world, data and its information have significance, and there are different implementations taking place to store it in different ways.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
